| Gagata | |
|---|---|
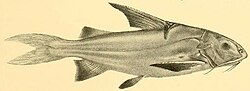
| |
| Gagata cenia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Siluriformes |
| Family: | Sisoridae |
| Subfamily: | Sisorinae |
| Genus: | Gagata Bleeker, 1858 |
| Type species | |
| Pimelodus gagata Hamilton, 1822
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Callomystax Günther, 1864 | |
Gagata is a genus of sisorid catfishes native to Asia.
Species
[edit]There are currently eight recognized species in this genus:[1]
- Gagata cenia (Hamilton, 1822)
- Gagata dolichonema (He, 1996)
- Gagata gagata (Hamilton, 1822)
- Gagata itchkeea (Sykes, 1839)
- Gagata melanopterus (Roberts & Ferraris, 1998)
- Gagata pakistanica (Mirza, Parveen & Javed, 1999)
- Gagata rhodobarbus Bhakat & Sinha, 2019
- Gagata sexualis (Tilak, 1970)
Gagata youssoufi may be synonymous with Gagata sexualis.[2]
Distribution
[edit]Gagata species are distributed in the Indus drainage in Pakistan and India, east and south (including peninsular India) to the Tenasserim drainages in Burma. G. cenia originates from the Indus, Mahanadi, Ganges, and Brahmaputra drainages in Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, Burma and possibly Nepal; it is also reported from the Irrawaddy drainage and Salween drainage.[3] G. dolichonema inhabits the upper Salween River basin in China and the Irrawaddy, Salween, and Tenasserim River basins in Burma.[4] G. gagata is from the Ganges drainage in India and Bangladesh and is reported from the Brahmaputra and Irrawaddy drainages. G. itchkeea is known from the Narmada, Krishna, and Cauvery drainages in peninsular India, though its presence in the Cauvery needs to be confirmed. G. melanoptera is distributed in the Irrawaddy, Rangoon, Sittang, and lower Salween drainages in Burma. G. pakistanica is from the Indus drainage in Pakistan. G. sexualis originates from the Ganges and Brahmaputra drainages in India, Bangladesh and Nepal.[3]
Description
[edit]Gagata species have a compressed head, eyes on side of the head, a depressed snout, small conical teeth in lower jaw, branchiostegal membranes broadly fused to isthmus, no serrations on anterior margin of pectoral spine but serrate posteriorly, no well-developed maxillary barbel membrane, outer and inner mental barbels close together with their origins nearly parallel in a transverse line, short nasal and maxillary barbels, and a lack of palatal teeth.[3]
Gagata species have a great range in lengths, from 5.8 centimetres (2.3 in) TL in G. sexualis and 7.6 cm (3.0 in) TL in G. itchkeea, to 15.0 cm (5.9 in) SL in G. cenia and 15.8 cm (6.2 in) SL in G. melanoptera, to 30.5 cm (12.0 in) TL in G. gagata.[5][6][7][8][9][10]
References
[edit]- ^ Fricke, Ron; Eschmeyer, William N. & van der Laan, Richard (eds.). "Species in the genus Gagata". Catalog of Fishes. California Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 21 August 2025.
- ^ Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2025). "Gagata youssoufi". FishBase.
- ^ a b c Thomson, Alfred W.; Page, Lawrence M. (2006). "Genera of the Asian Catfish Families Sisoridae and Erethistidae (Teleostei: Siluriformes)" (PDF). Zootaxa. 1345: 1–96. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.1345.1.1.
- ^ Ferraris, Carl J. Jr. (2007). "Checklist of catfishes, recent and fossil (Osteichthyes: Siluriformes), and catalogue of siluriform primary types" (PDF). Zootaxa. 1418: 1–628. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.1418.1.1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2022-03-11. Retrieved 2007-07-21.
- ^ Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Gagata sexualis". FishBase. July 2007 version.
- ^ Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Gagata itchkeea". FishBase. July 2007 version.
- ^ Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Gagata cenia". FishBase. July 2007 version.
- ^ Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Gagata melanopterus". FishBase. July 2007 version.
- ^ Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Gagata gagata". FishBase. July 2007 version.
- ^ Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Gagata youssoufi". FishBase. July 2014 version.