 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1E)-N,N′-Bis(4-ethoxyphenyl)ethanimidamide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H22N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 298.386 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Phenacaine, also known as holocaine,[1] is a local anesthetic. It is approved for ophthalmic use.[2]
Synthesis
[edit]The synthesis of phenacaine begins with the condensation of p-phenetidine (1) with triethyl orthoacetate (2) to afford the imino ether (a Pinner salt, 3). Reaction of that intermediate with a second equivalent of the aniline results (4) in a net displacement of ethanol, probably by an addition-elimination scheme, producing the amidine, phenacaine (5).
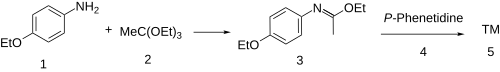
In the patented synthesis,[4] phenacetin was used as precursor. Treatment with phosphorus trichloride (PCl3) gave the enol chloride, and reaction of this intermediate with p-phenetidine then completed the synthesis of phenacaine.
References
[edit]- ^ "Holocaine Hydrochloride".
- ^ Merck Index, 1985
- ^ DeWolfe, Robert H. (1962). "Reactions of Aromatic Amines with Aliphatic Ortho Esters. A Convenient Synthesis of Alkyl N-Arylimidic Esters". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 27 (2): 490–493. doi:10.1021/jo01049a036.
- ^ DE 79868, Ernst Taeuber, issued 1894