Introduction

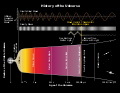
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is the branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole.
Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptians, Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars.
Professional astronomy is split into observational and theoretical branches. Observational astronomy is focused on acquiring data from observations of astronomical objects. This data is then analyzed using basic principles of physics. Theoretical astronomy is oriented toward the development of computer or analytical models to describe astronomical objects and phenomena. These two fields complement each other. Theoretical astronomy seeks to explain observational results and observations are used to confirm theoretical results.
Astronomy is one of the few sciences in which amateurs play an active role. This is especially true for the discovery and observation of transient events. Amateur astronomers have helped with many important discoveries, such as finding new comets. (Full article...)
General images -
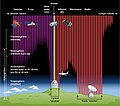
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated 1022 to 1024 stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye—all within the Milky Way galaxy.
A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material largely comprising hydrogen, helium, and traces of heavier elements. Its total mass mainly determines its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due to the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core. This process releases energy that traverses the star's interior and radiates into outer space. At the end of a star's lifetime, fusion ceases and its core becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or—if it is sufficiently massive—a black hole. (Full article...)
Did you know -
- ... that the Lone Signal project sends messages by ordinary citizens to extraterrestrial civilizations using the Jamesburg Earth Station?
- ... that 6Q0B44E, a recently discovered satellite of Earth, is thought to be a large piece of space debris?
- ... that approximately one-third of nearby galaxies contain low-ionization nuclear emission-line regions?
- ... that lunar lava tubes could provide natural shelters for manned lunar habitats?
- ... that many geographic features on Campbell Island, New Zealand, were named for members of the French 1874 Transit of Venus astronomical expedition?
More Did you know (auto generated)

- ... that in many works of fiction, the asteroid belt is the remnants of a destroyed planet?
- ... that two competing hypotheses seek to explain the unusual orbit of the exoplanet Nu Octantis Ab?
- ... that Na drugą planetę, published in 1895 as one of the earliest Polish science-fiction novels, was later criticized by communist-era censors for its perceived "adoration for America"?
- ... that a profile of artist Mark Hearld said his "wrens and squirrels, field mice and owls" help a child care about the planet better than telling them it is burning?
- ... that some exoplanets are evaporating catastrophically?
- ... that the Passive Seismic Experiment Package recorded one of the first instances of humans littering on another planetary body?
WikiProjects
Selected image -

Hubble Space Telescope image of NGC 6052, discovered on 11 June 1784 by William Herschel. The two components of NGC 6052 are designated NGC 6052A and NGC 6052B are attracted by each other's gravity, have collided and are interacting with each other.
Astronomy News
- 23 June 2025 –
- The Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile releases the first light images from its new 8.4-meter (28 ft) telescope. (Scientific American)
November anniversaries
- 2 November 1917 – The Hooker Telescope at Mount Wilson Observatory, the largest telescope in the world from 1917 until 1948, sees first light
- 14 November 1971 – Unmanned probe Mariner 9 arrives at Mars and becomes the first spacecraft to orbit around another planet
- 18 November 1989 – Explorer 66, a satellite designed to study cosmic microwave background radiation and supply evidence in support of the Big Bang theory, is launched
- 20 November 1998 – Zarya, the first module of the International Space Station, is launched
- 28 November 1967 – PSR B1919+21 becomes the first pulsar to be observed when it is discovered by Jocelyn Bell Burnell and Antony Hewish
Space-related Portals
Astronomical events
All times UT unless otherwise specified.
| 5 November, 12:36 | Southern Taurids peak |
| 5 November, 13:19 | Full moon |
| 5 November, 22:29 | Moon at perigee |
| 12 November, 11:52 | Northern Taurids peak |
| 17 November, 18:10 | Leonids peak |
| 20 November, 02:48 | Moon at apogee |
| 20 November, 08:47 | New moon |
| 20 November, 09:20 | Mercury at inferior conjunction |
| 21 November, 12:33 | Uranus at opposition |
| 29 November, 12:29 | Mars southward equinox |
Topics
Subcategories
Things you can do
|
Here are some Open Tasks :
Astronomy featured article candidates:
Astronomy articles for which peer review has been requested:
|
Wikibooks

These books may be in various stages of development. See also the related Science and Mathematics bookshelves.
- Astronomy
- GAT: A Glossary of Astronomical Terms
- Introduction to Astrophysics
- General relativity
- Observing the Sky from 30°S
- Observing the Sky from 40°N
Wikijunior
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus