| Yawelmani | |
|---|---|
| Yowlumne | |
| Yawʼlamnin ṭeexil | |
 Yawelmani sentence documented by A. L. Kroeber | |
| Pronunciation | [jawˀlamnin ʈɛːxil] |
| Native to | California |
| Region | Kern River |
Native speakers | 20–25 (2007, fluent and semispeakers)[1] |
Yok-Utian ?
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | None |
 Historical distribution of Yawelmani | |

Yawelmani Yokuts (also spelled Yowlumne and Yauelmani) is an endangered dialect of Southern Valley Yokuts historically spoken by the Yokuts living along the Kern River north of Kern Lake in the Central Valley of California.[2] Today, most Yawelmani speakers live on or near the Tule River Reservation.[3]
Name
[edit]Academic sources frequently use the name Yawelmani while referring to the language, though tribe members more often use the name Yowlumne.[3] The difference in terminology comes from the language itself, where the form Yowlumne is singular and Yawelmani is the paucal form, that is, it refers to a small group.[3]: 5 An increasing number of academic sources, including Weigel (2005), have opted to use Yowlumne instead, as the use of Yawelmani can be regarded as a misnomer.[3]: 5 [a]
When referencing their language, modern speakers of Yawelmani use the terms inyana (Indian), and yaw'lamnin ṭeexil (speech of the Yowlumne).[3]: 5
Speakers
[edit]A 2011 estimate by Victor Golla placed the number of fluent and semi-fluent Yawelmani speakers at "up to twenty-five."[4]
Revitalization efforts
[edit]In 1993, the Master-Apprentice Language Learning Program piloted a series of language programs that included Yawelmani. The program was reportedly effective in teaching conversational Yawelmani to tribal members without prior knowledge and increasing language use among elders.[5]
Phonology
[edit]Consonants
[edit]| Bilabial | Dental | Retroflex | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stop | plain | p /p/ | t /t/ | ṭ /ʈ/ | k /k/ | ʼ /ʔ/ | |
| aspirated | ph /pʰ/ | th /tʰ/ | ṭh /ʈʰ/ | kh /kʰ/ | |||
| ejective | pʼ/pʼ/ | tʼ/tʼ/ | ṭʼ /ʈʼ/ | kʼ /kʼ/ | |||
| Affricate | plain | c /t͡s/ | c̣ /t͡ʂ/ | ||||
| aspirated | ch /t͡sʰ/ | c̣h /t͡ʂʰ/ | |||||
| ejective | cʼ /t͡sʼ/ | c̣ʼ /t͡ʂʼ/ | |||||
| Fricative | s /s/ | ṣ /ʂ/ | x /x/ | h /h/ | |||
| Nasal | plain | m /m/ | n /n/ | ||||
| glottalized | mʼ /mˀ/ | nʼ /nˀ/ | |||||
| Approximant | plain | w /w/ | l /l/ | y /j/ | |||
| glottalized | wʼ /wˀ/ | lʼ /lˀ/ | yʼ /jˀ/ | ||||
- Sounds /t͡ʂ, t͡ʂʰ, t͡ʂʼ/ may be heard freely as postalveolar [t͡ʃ, t͡ʃʰ, t͡ʃʼ] among speakers.[8]
Vowels
[edit]Yawelmani has 10 vowel phonemes:[6]: 19
| Unrounded | Rounded | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| short | long | short | long | |
| High | i | iː | u | uː |
| Mid | ɛ | ɛː | ɔ | ɔː |
| Low | a | aː | ||
- There are 5 short-long vowel pairs.
- Short high vowels may become more centralized in fast speech: /i/ → [ɪ], /u/ → [ʊ].
- Long high vowels are almost always lower than their short counterparts: /iː/ → [ɛː], /uː/ → [ɔː].
- All long vowels may be shortened by a phonological process. Thus, a single long vowel has two different phonetic realizations:
- /iː/ → [ɛ, ɛː],
- /ɛː/ → [ɛ, ɛː],
- /aː/ → [a, aː],
- /uː/ → [ɔ, ɔː],
- /ɔː/ → [ɔ, ɔː].
- Note that the high long vowel /uː/ is usually pronounced the same as /ɔ/ and /ɔː/.
- Note that the high long vowel /iː/ is usually pronounced the same as /ɛ/ and /ɛː/.
As can be seen, Yawelmani vowels have a number of different realizations (phones) which are summarized below; [ɪ] and [ʊ] are variants in rapid speech of /i/ and /u/, respectively:[6]: 19
| Front | Back | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| short | long | short | long | |
| High | i | u | ||
| Near-high | ɪ | ʊ | ||
| Mid | ɛ | ɛː | ɔ | ɔː |
| Low | a | aː | ||
Syllable & phonotactics
[edit]The Yawelmani syllables can be either a consonant-vowel sequence (CV), such as in wa 'however', or a consonant-vowel-consonant sequence (CVC), such as in xat 'eating, food'.[6]: 26,95,238 Thus the generalized syllable is the following:
- CV(C)
Verbal roots[b] are disyllabic and have either one of two shapes:[6]: 26
- CV.CV
- CV.CVC
Outside of verbal roots, more complex phonotactic forms are also permitted, so long as each syllable has the structure CV(C).[6]: 26–27
Restrictions exist on the distribution of certain glottalized consonant phonemes in surface form: glottalized nasals and approximants cannot appear word-initially or after another consonant; if they would otherwise appear after another consonant, they lose their glottalized quality.[6]: 19
Phonological processes
[edit]Vowel shortening
[edit]When long vowels are in closed syllables, they are shortened:
/p’a.xaː.t’it/ → [p’axaːt’it] p̓axaat̕it 'mourn (passive aorist)' (/aː/ remains long) /p’a.xaːt’.hin/ → [p’axat’hin] p̓axat̕hin 'mourn (aorist)' (/aː/ is shortened) /ts’u.juː.hun/ → [ts’ujɔːhun] c̓uyoohun 'urinate (aorist)' (/uː/ remains long) /ts’u.juːt/ → [ts’ujɔt] c̓uyot 'urinate (passive aorist)' (/uː/ is shortened)
Vowel harmony
[edit]Yawelmani has suffixes that contain either an underspecified high vowel /I/ or an underspecified non-high vowel /A/.
- Underspecified /I/ will appear as /u/ following the high rounded vowel /u/ and as /i/ following all other vowels /i, a, ɔ/:
/-hIn/ -hun/-hin (aorist suffix) /muʈhIn/ → [muʈhun] muṭhun 'swear (aorist)' /ɡij’hIn/ → [ɡij’hin] giy̓hin 'touch (aorist)' /ɡɔphIn/ → [ɡɔphin] gophin 'take care of infant (aorist)' /xathIn/ → [xathin] xathin 'eat (aorist)'
- Underspecified /A/ will appear as /ɔ/ following the non-high rounded vowel /ɔ/ and as /a/ following all other vowels /i, u, a/:
/-tAw/ -tow/-taw (nondirective gerundial suffix) /ɡɔptAw/ → [ɡɔptɔw] goptow 'take care of infant (nondir. ger.)' /ɡij’tAw/ → [ɡij’taw] giy̓taw 'touch (nondir. ger.)' /muʈtAw/ → [muʈtaw] muṭtaw 'swear (nondir. ger.)' /xattAw/ → [xatːaw] xattaw 'eat (nondir. ger.)'
Vowel epenthesis
[edit]Yawelmani adds vowels to stems, when suffixes with an initial consonant are affixed to word with two final consonants in order to avoid a triple-consonant-cluster.
Grammar
[edit]Case system
[edit]Yawelmani is a primary object language.[3]
A. L. Kroeber documented the language's case system in his 1907 paper The Yokuts Language of South Central California.[9]
| Objective | Noun | -a (-i) |
| Demonstrative | -n, -in | |
| (plural), Pronoun | -wa | |
| Possessive | -in | |
| Instrumental | -ni | |
| Locative | -u | |
| Ablative | -nit |
In his 1944 grammar of the Yokuts language, Newman analyzed the case system in greater depth, taking care for the different realizations of the case suffixes with nouns based primarily on the phonotactic profile of the root or stem to which the nouns attach, as in the table below.[6] Note that the forms represent the basic case suffixes; in Newman's analysis, vowel harmony with the preceding syllable may apply as appropriate. Elements in parentheses are analyzed by Newman to be added to the root in preparation for the affix (which he terms an "inorganic protective element"),[6]: 11 rather than forming part of the affix itself. Moreover, Newman treats the CV:C category (his IAb type) as generally a variant of CVC (his IAa type), except for two unique members of the CV:C class, yeet'- 'one' and mooṣ- 'sweathouse'.[6]: 175
| Subjective | Objective | Possessive | Indirect Objective | Ablative | Locative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVC (IAa) | - | -i, -a | -in | (V:)-ni | (V:)-nit | (V)-w |
| CV:C (IAb) | - | - | -in | -ni | -nit | (V)-w |
| CV: (IBa) | (')- | (')-in, (')-an | (')-in | -ni | -nit | -w |
| CV: verb nominalizations (IBb) | (')- | -i, -a | (')-in | -ni | -nit | -w |
| CV.CVC (IIA) | - | -i, -a | -in | (V:)-ni | (V:)-nit | (V)-w |
| CV.CV:C (IIBa) | - | -, -i, -a | -in | -ni | -nit | (V)-w |
| CV.CV:C variant form (IIBb) | - | - | -in | -ni | -nit | (V)-w |
| CV.CV:C limited set of words (IIBc) | - | -i, -a | -in | (V:)-ni | (V:)-nit | (V)-w |
Examples of these paradigms are provided in the following table.
| Word root | Subjective | Objective | Possessive | Indirect Objective | Ablative | Locative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVC (IAa) | pil 'road' | pil | pila | pilin | pilni or pilaani | pilnit or pilaanit | pilaw |
| CV: (IBa) | samaa 'mouth' | sama' | samaa'in | samaa'in | samaani | samaanit | samaw |
| CV: verb nominalizations (IBb) | damnaa 'act of trying' | damna' | damna | damnin | damnaani | damnaanit | damnaw |
| CV.CVC (IIA) | biwiineelis 'one who is made to sew' | biwiineelis | biwiinelsi | biwiinelsin | biwiinelseeni | biwiinelseenit | biwiinelsiw |
| CV.CV:C (IIBa) | lagaa'eey 'a place for staying overnight' | lagaa'iy | lagaa'ey | lagaa'eeyin | lagaa'eyni | lagaa'eyni | lagaa'eeyaw |
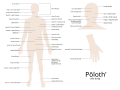
Selected vocabulary
[edit]-
Yawelmani anatomy
-
Yawelmani kinship terms
Notes
[edit]- a These include, for example, Kiparsky (2023).[10]
- b That is, "bases" in Newman's (1944) sense.[6]: 26
References
[edit]- ^ Yokuts at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ^ Whistler, Kenneth W.; Golla, Victor (1986). "Proto-Yokuts Reconsidered". International Journal of American Linguistics. 52 (4): 317–358. doi:10.1086/466028. ISSN 0020-7071. JSTOR 1265536. S2CID 144822697.
- ^ a b c d e f Weigel, William (2005). Yowlumne in the Twentieth Century (PhD thesis). University of California, Berkeley.
- ^ Golla, Victor (2011-08-02). California Indian Languages. University of California Press. ISBN 9780520266674.
- ^ "Survival of Endangered Languages: The California Master-Apprentice Program". International Journal of the Sociology of Language (123): 177–191. 2009. doi:10.1515/ijsl.1997.123.177. ISSN 1613-3668.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Newman, Stanley (1944). Yokuts Language of California. New York: The Viking Fund. Retrieved 4 October 2025.
- ^ Newman, Stanley S. (1946). The Yawelmani Dialect of Yokuts. In Harry Hoijer (ed.), Linguistic Structures of Native America: New York: Viking Fund. pp. 222–248.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: publisher location (link) - ^ Golla, Victor (2011). California Indian Languages. University of California Press.
- ^ Kroeber, A. L. (1907). "The Yokuts Language of South Central California" (PDF). University of California Publications in American Archaeology and Ethnography: 281.
- ^ Kiparsky, Paul (2023). "A Stratal Optimality Theory perspective on vowel harmony" (PDF). In van der Hulst, Harry; Ritter, Nancy A. (eds.). The Oxford Handbook of Vowel Harmony. pp. 192–219. Retrieved 4 October 2025.